the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
Gridded maps of geological methane emissions and their isotopic signature
Giancarlo Ciotoli
Stefan Schwietzke
Martin Schoell
Methane (CH4) is a powerful greenhouse gas, whose natural and anthropogenic emissions contribute ∼20 % to global radiative forcing. Its atmospheric budget (sources and sinks), however, has large uncertainties. Inverse modelling, using atmospheric CH4 trends, spatial gradients and isotopic source signatures, has recently improved the major source estimates and their spatial–temporal variation. Nevertheless, isotopic data lack CH4 source representativeness for many sources, and their isotopic signatures are affected by incomplete knowledge of the spatial distribution of some sources, especially those related to fossil (radiocarbon-free) and microbial gas. This gap is particularly wide for geological CH4 (geo-CH4) seepage, i.e. the natural degassing of hydrocarbons from the Earth's crust. While geological seepage is widely considered a major source of atmospheric CH4, it has been largely neglected in 3-D inverse CH4 budget studies given the lack of detailed a priori gridded emission maps. Here, we report for the first time global gridded maps of geological CH4 sources, including emission and isotopic data. The maps include the four main categories of natural geo-CH4 emission: (a) onshore hydrocarbon macro-seeps, including mud volcanoes, (b) submarine (offshore) seeps, (c) diffuse microseepage and (d) geothermal manifestations. An inventory of point sources and area sources was developed for each category, defining areal distribution (activity), CH4 fluxes (emission factors) and its stable C isotope composition (δ13C-CH4). These parameters were determined considering geological factors that control methane origin and seepage (e.g. petroleum fields, sedimentary basins, high heat flow regions, faults, seismicity). The global geo-source map reveals that the regions with the highest CH4 emissions are all located in the Northern Hemisphere, in North America, in the Caspian region, in Europe and in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf. The globally gridded CH4 emission estimate (37 Tg yr−1 exclusively based on data and modelling specifically targeted for gridding, and 43–50 Tg yr−1 when extrapolated to also account for onshore and submarine seeps with no location specific measurements available) is compatible with published ranges derived using top-down and bottom-up procedures. Improved activity and emission factor data allowed previously published mud volcanoes and microseepage emission estimates to be refined. The emission-weighted global mean δ13C-CH4 source signature of all geo-CH4 source categories is about −49 ‰. This value is significantly lower than those attributed so far in inverse studies to fossil fuel sources (−44 ‰) and geological seepage (−38 ‰). It is expected that using this updated, more 13C-depleted, isotopic signature in atmospheric modelling will increase the top-down estimate of the geological CH4 source. The geo-CH4 emission grid maps can now be used to improve atmospheric CH4 modelling, thereby improving the accuracy of the fossil fuel and microbial components. Grid csv (comma-separated values) files are available at https://doi.org/10.25925/4j3f-he27.
- Article
(10064 KB) - Full-text XML
-
Supplement
(3695 KB) - BibTeX
- EndNote
Methane (CH4) is a powerful greenhouse gas, whose concentrations in the atmosphere have increased about 2.5 times since the pre-industrial era (1750), approaching 1.9 ppm in 2018. With a global emission of about 558 Tg CH4 yr−1 (Saunois et al., 2016), CH4 contributes ∼20 % to global radiative forcing (Ciais et al., 2013). The CH4 budget, i.e. natural and anthropogenic sources and sinks, estimated by either bottom-up (emission inventories and process-based models) or top-down (inverse modelling) approaches (e.g. Saunois et al., 2016 and Refs. therein), is subject to considerable uncertainties, however. With respect to natural sources, top-down estimates show strong disagreement with bottom-up estimates, both globally and regionally. Global box modelling based on isotopic measurements (stable C isotope ratio, δ13C-CH4) of source signatures and the atmosphere combined with three-dimensional (3-D) forward modelling using trends and spatial gradients recently improved the knowledge of major sources (fossil-fuel, agriculture and wetlands) and their spatial–temporal variation (e.g. Schwietzke et al., 2016). Nevertheless, isotopic data lack representativeness of CH4 source signatures for many sources, and source attributions are limited by incomplete knowledge of the spatial distribution of some major sources, especially fossil fuel and microbial. In this respect, geological CH4 (geo-CH4) emissions, i.e. the natural component of fossil fuel (14C-free) emission, play a critical role. Geological CH4 sources are from the natural degassing of hydrocarbons from the Earth's crust (e.g. Etiope and Klusman, 2002; Kvenvolden and Rogers, 2005; Etiope, 2015). Geo-CH4 originates in deep rocks by biotic (i.e. microbial and thermogenic) processes related to petroleum fields in sedimentary basins, as described in a wide body of petroleum geology literature (see, for example, Etiope, 2017 for a recent overview). Relatively minor amounts of CH4 can also be produced by abiotic processes, which do not involve organic matter in rocks (e.g. magma degassing, high temperature post-magmatic process, CO2 hydrogenation or Sabatier reaction, in geothermal–volcanic systems and ultramafic igneous rocks; e.g. Etiope and Sherwood Lollar, 2013). Surface emissions of geological CH4 occur through the process known as “gas seepage”, which includes point sources (gas–oil seeps, mud volcanoes (MVs), springs, geothermal manifestations (GMs)) and area sources (diffuse “microseepage”, MS). Once considered a minor natural CH4 source globally (e.g. Lelieveld et al., 1998; Prather et al., 2001), geological degassing is today recognised as a major contributor to atmospheric CH4, as indicated by the agreement between bottom-up and top-down estimates converging to 40–60 Tg yr−1 (Etiope et al., 2008a; Ciais et al., 2013; Etiope, 2015; Saunois et al., 2016; Schwietzke et al., 2016). Nevertheless, geological seepage has mostly been neglected in global top-down CH4 budget studies (e.g. Bousquet et al., 2006; Bergamaschi et al., 2013). In addition, geological CH4 has erroneously been considered to be typically 13C-enriched, thus with relatively high δ13C-CH4 values compared to biological sources such as wetlands (a global average of −38 ‰ was assumed for seepage by Sapart et al., 2012). In petroleum geochemistry it is well known, in fact, that in addition to the common thermogenic gas produced by moderate to high maturity source rocks, typically with δ13C-CH4 from −30 ‰ to about −50 ‰, vast amounts of methane in sedimentary basins are microbial (thus with δ13C-CH4 ranging from −55 ‰ to about −90 ‰) and thermogenic from low maturity source rocks, with δ13C-CH4 from −50 ‰ to about −70 ‰ (Etiope, 2017; Milkov and Etiope, 2018). Degassing (seepage) to the atmosphere of 13C-depleted geo-CH4 sources is also widely documented (e.g. Etiope et al., 2009 and references therein). In addition to using unrepresentatively heavy δ13C-CH4 geo-CH4 values in previous studies, detailed a priori gridded maps of geo-CH4 emissions and its isotopic signatures, which are essential for 3-D inverse modelling and for the discrimination between natural and anthropogenic microbial emissions, are currently lacking.
Here, we report the first global grid maps of geological CH4 sources, including emissions and isotopic source signatures. The maps, elaborated by ArcGIS at resolution, include the four main categories of natural geological CH4 sources: (a) onshore hydrocarbon macro-seeps (including mud volcanoes), (b) submarine (offshore) seeps (SSs), (c) diffuse microseepage and (d) geothermal manifestations. For each category we have developed an inventory of point sources and area sources, including coordinates (areal distribution, i.e. activity), estimated CH4 fluxes (emission factors) and δ13C-CH4 values. These parameters have been determined considering several geological factors that control CH4 origin and seepage (petroleum fields, sedimentary basins, faults, earthquakes, geothermal–volcanic systems), based on published and originally ad hoc developed datasets, as described in Sects. 4, 5, 6 and 7. Integrated (total geo-CH4) maps and associated text files (csv, comma-separated values) have been generated to facilitate atmospheric CH4 modelling to improve the accuracy of fossil fuel and microbial components. Gridded geo-CH4 emissions were compared with published global estimates, derived using different approaches (e.g. Etiope et al., 2008; Etiope, 2012, 2015; Schwietzke et al., 2016). Gridded emissions do not necessarily represent the actual global geo-CH4 emission or improve previous estimates because the datasets developed for the gridding may not be complete or may not contain all the information necessary for improving previous estimates. A refinement of bottom-up estimates has only been possible for mud volcanoes and microseepage because their gridding implied a careful assessment of the spatial distribution and emission factors.
Geological CH4 sources can be classified into four major categories:
- a.
onshore hydrocarbon seeps (or macro-seeps) in sedimentary (petroliferous) basins, including CH4-rich gas–oil seeps, mud volcanoes (MVs) and gas-bearing springs, hereafter referred to as OSs;
- b.
submarine (offshore) seeps, where CH4 released from the shallow seafloor (coastal areas or shelves, generally up to 300–400 m b.s.l.) can cross the water column and enter the atmosphere, hereafter referred to as SSs; deep-sea seeps that are unlikely responsible for methane emission into the atmosphere are not considered;
- c.
diffuse microseepage in sedimentary (petroliferous) basins, the widespread, invisible exhalation of CH4 typically detected in correspondence with gas–oil fields, hereafter referred to as MS;
- d.
geothermal and volcanic manifestations, where CH4 is a minor component (subordinated to CO2) but with potentially significant fluxes to the atmosphere, hereafter referred to as GMs.
These geological methane sources are extensively described and discussed in a wide body of literature; for details and definitions the reader may refer to Etiope and Klusman (2002); Judd (2004); Kvenvolden and Rogers (2005); Etiope et al. (2007); Judd and Hovland (2007); Etiope et al. (2008); Etiope and Klusman (2010); Etiope (2015), Mazzini and Etiope (2017). Their global bottom-up and top-down emissions, compared with other natural CH4 sources, are summarized in Fig. 1.
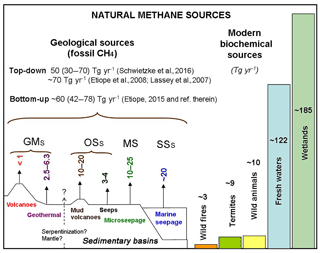
Figure 1Sketch of geo-CH4 sources, their global emission estimates (after Etiope, 2012; and Etiope, 2015) and comparison with other natural CH4 sources (bottom-up estimates from Saunois et al., 2016). GMs: geothermal manifestations, OSs: onshore seeps, MS: microseepage and SSs: submarine seeps.
Methods for creating CH4 emission and δ13C-CH4 grids vary by geo-CH4 category, based on the data availability and specific seepage characteristics. Methods are therefore described in detail for each category in Sects. 4 (OSs), 5 (SSs), 6 (MS) and 7 (GMs). First, a brief overview of the different types of input data and gridding procedure is given below.
3.1 Data sources
Table 1 summarizes how the four categories of geo-CH4 sources were elaborated, showing data sources, the parameters used to define the “activity” (spatial distribution), the “emission factors” (fluxes) and the attribution of the isotopic CH4 values. The list and web links of the sources of databases are reported in the Supplement (Sect. S6).
3.2 Gridding procedure
The gridding procedure is the same for each geo-CH4 source category. Geo-CH4 emission and isotope datasets were imported in an ArcGIS environment and saved in either point (OS and GM) or polygon (SS and MS) shapefile format, including coordinates and attributes (i.e. type of emission, area, emission factor, isotopic CH4 values, plus geographical information, such as country and region). The grid was then joined with single OS, SS, MS and GM shapefiles. The final csv files include data fields that define the coordinates of each cell centroid, the variable name and its unit of measurement (t yr−1 per cell for CH4 emission and ‰ for δ13C-CH4, according to VPDB, Vienna Pee Dee Belemnite, standard). For the grid cell values, the number zero (0) is used to indicate an actual or best emission estimate of zero (no seepage), whereas −9999 indicates lack of knowledge of the emission. Specifically, in the CH4 output files, the following are used.
-
A zero (0) value is used for
-
all offshore cells of the onshore seepage shape files (OS, MS and GM);
-
all onshore cells of the offshore seepage (SSs);
-
all onshore cells outside the potential MS area;
-
onshore cells without OS or GM sources;
-
offshore cells outside the SS areas.
-
-
The number −9999 is used for
-
cells within SS areas where emissions are unknown.
-
The categories OS, MS and GM, due to the method of emission derivation (see related sections below), always have an emission value.
In the isotope files, the following points are considered:
-
An isotopic value is reported in each cell that has a flux value.
-
Where specific values are not available (as occurred for OSs and SSs), the global weighted average δ13C for the relative emission category is reported.
-
Four decimals are used for global weighted average isotope values; this can help to trace back which cells are based on cell-specific data (with one decimal), and which contain weighted averages (four decimals).
-
The value −9999 is only used for cells with no emissions in the corresponding CH4 output files.
The application of such rules is described in the specific chapters of the four emission categories. Once individual OS, SS, MS and GM maps/files were produced, they were merged into a unified, total geo-CH4 gridded map: emissions per cell were summed and δ13C values were averaged.
4.1 Global seep count and distribution
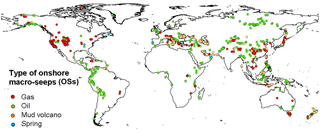
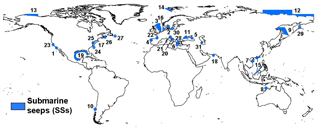
The spatial distribution (activity) of onshore seeps is derived from geographic coordinates of 2827 seeps, from 89 countries, reported in a global onshore seep dataset, which includes 1119 oil seeps, 846 gas seeps, 741 mud volcanoes and 121 gas-bearing springs. This dataset is an updated version of a previous inventory (named GLOGOS, reporting 2100 seeps) available from CGG (2015) and described in Etiope (2015). The global distribution of OSs is reported in Fig. 2.
The seeps listed in the dataset generally refer to individual focused vents (single macro-seep manifestations), but in several cases they refer to groups or clusters, or even wide zones of multiple seep points. A total of 612 seeps (569 gas–oil seeps and 43 mud volcanoes) could not be geographically located with precision and they are listed without coordinates (in addition to the 2827 seeps). The dataset, therefore, actually mentions a total of 3439 seeps or seepage sites, including 3396 gas–oil seeps and 784 mud volcanoes. The total number of 3439 OSs represents about 30 % of total seeps assumed to exist on Earth (≈10 000 was proposed by Clarke and Cleverly, 1991), but the present dataset includes the largest and more active seeps (especially for MVs) because they are more easily documented and have attracted attention for scientific research, petroleum exploration and natural heritage protection. Small or inactive seeps tend to be less observed and reported. In particular, the MV inventory is almost complete, probably missing smaller MVs in Asia. The gas–oil seeps in the dataset likely contribute more than 50 % of the previously estimated total gas–oil seep emission. Africa and South America likely host a larger number of gas–oil seeps and springs not documented in the dataset because of the paucity of specific investigations, especially in remote areas.
4.2 Attribution of CH4 emissions to individual seeps
The attribution of CH4 emission magnitudes to individual seep locations follows two different approaches for (a) gas–oil seeps or springs and (b) mud volcanoes (MVs).
4.2.1 Emission of gas–oil seeps and springs
Direct measurements of CH4 flux are available for about 100–200 gas–oil seeps in Europe, Asia and North America (see Table 6.1 in Etiope, 2015). In general, therefore, potential or theoretical flux values have been attributed to the inventoried seeps. Theoretical emission values can be reasonably provided only in terms of order of magnitude (i.e. 100, 101, 102, 103, 104 t yr−1). For gridding purposes, however, theoretical values (approximate working values) were used taking into account basic characteristics of the several seeps, i.e. the type of seep (for example, gas seeps generally release more methane than oil seeps) and the activity and size of the seep (according to specific literature, reports, web images), and taking into account experimental data as calibration, i.e. flux values measured in the field from seeps covering a wide range of activity and size (data are taken from the wide body of literature considered in Table 6.1 of Etiope, 2015). The theoretical values also take into account the gas emission from the invisible miniseepage, which is the diffuse degassing from the ground surrounding the macro-seep craters and vents (see definitions in Etiope, 2015), and that adds an amount of gas that is 3 times higher than that released from the macro-seep (Etiope, 2015). This resulted in the attribution of the values reported in Table S1. These values should be considered as first-order estimates and care should be taken when using individual seep flux estimates from this product to derive global emission estimates, as discussed in Sect. 4.5.
4.2.2 Emission of mud volcanoes (MVs)
For MVs, emission values refer to the continuous quiescent degassing; i.e. they do not include emissions during episodic eruptions, as these are practically impossible to estimate for each MV. Eruptions were considered separately for the global emission estimate as discussed below. The quiescent emissions were attributed to each MV following the activity (area) and emission factor approach as explained below.
A precise evaluation of the MV areas was performed using accurate image (Google Earth) analysis. For each MV visible on Google Earth images, the area of the entire MV structure, including central craters and flanks, was estimated by drawing a polygon encompassing the mud cover and mound flanks. For smaller MVs, not visible on low-resolution Google Earth images or covered by vegetation, photos or information from published literature or web sources were considered to define the order of magnitude of the MV size. From two repeated image analyses the global MV area resulted to be about 680±40 km2.
The MV emissions were then assessed using an updated dataset of fluxes measured from 16 MVs in Azerbaijan, Romania, Italy, Taiwan, China and Japan (Table S2), distinguishing between the macro-seepage (the focused emission from craters and vents) and miniseepage. Regression analysis between MV area, miniseepage and macro-seep flux of these measured MVs was used to derive miniseepage and macro-seep flux (and thus the total CH4 emission) for each MV of the inventory, whose area was determined as previously indicated. The procedure is described in detail in the Supplement (Sect. S1.1)
4.2.3 The “big emitters”
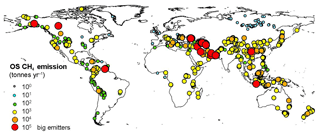
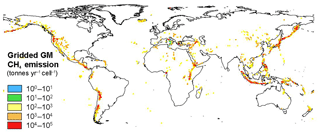
There is a total of 76 OSs with emissions in the order of 104 t CH4 yr−1 (i.e. that may emit at least 10 000 t CH4 yr−1 individually), and they can be considered big emitters. They typically refer to large, very active and frequently erupting MVs so their emission is estimated based on the emission factor and area approach described in the previous section. The 76 big emitters likely dominate the spatial distribution of CH4 emissions (they represent 63 % of the total OS emission) and the weighted global mean isotopic value. As shown in Fig. 3, it is clear that, on a global scale, the Caspian and Middle East regions represent the main OS emission areas.
4.3 Attribution of the δ13C-CH4 value
For each seep the δ13C-CH4 value is (a) measured, as indicated in the literature (available in the OS inventory; CGG, 2015), or (b) estimated on the basis of isotopic values, found from one of the following three sources, in priority order:
-
from similar seeps occurring in the same basin (when these data are available);
-
from reservoir gas in the same petroleum field, from the Sherwood et al. (2017) dataset or literature;
-
suggested by local petroleum geology (existence of microbial gas, thermogenic gas, oil), when the previous procedures cannot be applied.
The OS emission-weighted value (Sect. 4.5.2) was used for gridding where the isotopic value could not be assessed. The global distribution of three classes of δ13C-CH4 value is shown in Fig. S4.
4.4 OS gridding
The OS shapefile generated in ArcGIS was spatially joined to the vector square grid. OSs occur in 616 cells, for a total emission of 3.9 Tg yr−1 (Fig. 4). This is about 0.1 Tg yr−1 higher than the actual sum of the seep emission in the inventory because of multiple counting of 57 seeps that occur exactly on the boundary of a cell.
4.5 Evaluation of global OS emission and δ13C-CH4
4.5.1 Reassessing global OS emission
Because the OS inventory is not complete and the uncertainty of the theoretical flux values considered for individual oil–gas seeps is large (see Sect. 4.6), the OS flux grid is not meant to update or refine the previous global OS CH4 emission estimate (Etiope et al., 2008). A comparison with the published bottom-up estimates can establish whether the OS inventory data used in the OS flux grids are plausible. However, the procedure developed to attribute CH4 emissions to MVs can represent a refinement of the global MV emission estimate.
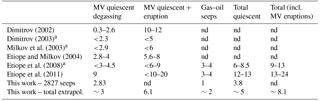
Published bottom-up estimates of CH4 emission from onshore macro-seeps are reported in Table 2. Some estimates included, without a clear distinction, shallow submarine MV (e.g. Dimitrov, 2003; Milkov et al., 2003), which must be considered within the category SSs in this work. Therefore, those estimates are indicated in the table as upper limits. Because the data of the OS inventory, as explained in Sect. 4.2, only refer to quiescent degassing, the table distinguishes emissions that exclude MV eruptions (quiescent degassing) and those that include MV eruptions.
Concerning gas–oil seeps and springs, the use of the theoretical values, as described in Sect. 4.2, results in global CH4 emission of about 1 Tg yr−1 (Table 2). As indicated in Sect. 4.1, the OS dataset, although representing only 30 % of all seeps existing on Earth, includes the largest and more active seeps, which may contribute at least 50 % of the global emission; accordingly, the total gas–oil seep emission could be likely around 2 Tg yr−1. Any further or more detailed extrapolation to a global seep emission estimate would be inappropriate.
The global MV emission from quiescent degassing, i.e. the sum of the MV emission values reported in the OS dataset, amounts to ∼2.8 Tg yr−1. The total CH4 emissions from the 2827 OSs is, therefore, about 3.8 Tg yr−1 (1+2.8 Tg yr−1). The OS–MV dataset likely represents about 90 % of total MVs assumed to exist on Earth (≈900; Dimitrov, 2002; Etiope and Milkov, 2004); extrapolating to the total MV number would result in a global MV emission of approximately 3 Tg yr−1. This is within the range suggested by Etiope and Milkov (2004). Compared to previous emission estimates of Etiope and Milkov (2004) and Etiope et al. (2011), the present MV estimate used a lower activity, i.e. lower global area, 680 km2 instead of 2800 km2 (which was suggested by data provided by the Azerbaijan Geological Institute), but relatively higher emission factors. Concerning the MV eruptions, we can only use, again, the rough estimations indicated in Dimitrov (2003), Milkov et al. (2003) and Aliyev et al. (2012) (i.e. average gas flux during eruptions of MVs in Azerbaijan 2.5×108 m3, the proportions of eruptive MVs 27 % and the frequency of eruption 1.35 eruptions yr−1), which translate into a total eruptive emission of 3.1 Tg yr−1 (Milkov et al., 2003). Therefore, the global OS emission, including MV eruptions and assuming the theoretical values for the gas–oil seeps and springs, would be ∼8.1 Tg yr−1, which is within 10 % of the lower range proposed by Etiope et al. (2008).
4.5.2 The average emission-weighted δ13C-CH4
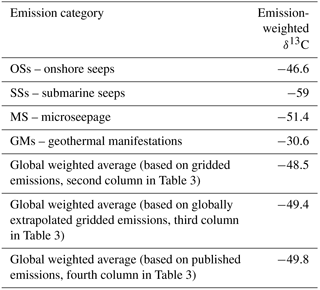
The total mean value of δ13C-CH4 from all OSs is −47.8 ‰, and that from the 76 big emitters is −46.7 ‰. The global OS emission-weighted mean value of δ13C-CH4 is −46.6 ‰.
4.6 OS uncertainties
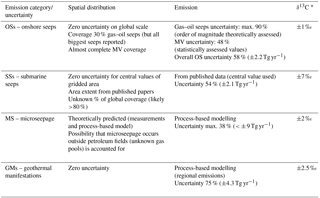
Spatial distribution uncertainty. In the grid, the uncertainty of the geographic distribution of the OSs is practically zero, as all identified seeps have geographic coordinates within an error <1∘.
Emission uncertainty. The uncertainty of the modelled oil–gas seep emission (based on the method of value attribution described in Sect. 4.2.1) is maximum 90 % (1±0.9 Tg yr−1). The uncertainty of global MV emission (48 %) was estimated by summing (a) the uncertainty of the estimated MV areas (6 %; see Sect. 4.2.2) and (b) the uncertainty of the modelled MV emission factor (42 %; see Sect. S1.1). Because oil–gas seeps and MVs account for 26 % and 74 % of total OS emission, respectively, the overall gridded OS emission uncertainty is about 58 % (3.8±2.2 Tg yr−1).
δ13C-CH4 uncertainty. The uncertainty of measured δ13C values (from literature) practically corresponds to laboratory analytical uncertainty (typically <0.1 ‰). The maximum uncertainty of the estimated δ13C values (based on criteria described in Sect. 4.3) is approximately within 15 ‰, i.e. half of the range of δ13C values for typical microbial (−80 ‰ to −60 ‰) and thermogenic (−50 ‰ to −20 ‰) gas. The uncertainty of the emission-weighted mean (−46.6 ‰) is mainly induced by the 76 big emitters, for which the δ13C values are available or estimated with good approximation (<±5 ‰), leading to a mean value of −46.7 ‰. The difference between global emission-weighted and 76 big emitters' average δ13C values is 0.1 ‰. The average order of magnitude of ±1 ‰ can be considered for the uncertainty of global emission-weighted δ13C value.
5.1 Assessment of global SS area
A specific dataset of offshore seepage areas, in coastal regions and shallow seas (typically <500 m deep, which is generally the maximum depth of seeps that may affect the atmosphere; e.g. Solomon et al., 2009), was developed based exclusively on published literature (Table S4). The dataset includes the following:
- a.
Submarine seeps (including mud volcanoes), where gas was observed to reach the sea surface via bubble plumes and the emission to the atmosphere was estimated, are included. Flux emission estimates are available from 15 zones (from focused, point-source, manifestations to wide regional areas) in the seas of Australia, Bulgaria, Brunei, Canada, Chile, China, Denmark, Georgia, Greece, Norway, Spain, Romania, Russia, Turkey, Ukraine, UK and USA.
- b.
Submarine seeps in shallow seas, where gas was actually observed (also through hydro-acoustic images) to reach the surface but the output to the atmosphere was not provided, or where, due to the shallow seabed (<400–500 m), the methane is expected to enter the atmosphere, are included. These areas (16 zones) are offshore of USA, Canada, Mexico, the Netherlands, Denmark, France, Italy, Greece, Russia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan and Pakistan.
The dataset does not include deep-sea seeps or areas with gas-charged sediments (e.g. as those inventoried by Fleischer et al., 2001) that may release methane into the water column, but for which the possibility of injection into the atmosphere is scarce or unknown. The area and methane flux estimates reported in several papers were used here without critical evaluation. Geo-referenced polygons were created for each area (Fig. 5).
5.2 Attribution of seepage levels
CH4 fluxes from the original publications (Table S4) are used in the gridded emission dataset.
5.3 Attribution of the δ13C value
The δ13C-CH4 values of SSs are attributed on the basis of available literature or considering the geological setting (type of petroleum system, origin of the gas) of the seepage areas (italic values in Table S4) following the same criteria adopted for OSs. For four areas in Table S4 (China–Brunei offshore, Laurentian Channel and Grand Banks Downing Basin in Canada and eastern Kamchatka Shelf in Russia) it was not possible to attribute any theoretical δ13C value because the gas may actually be derived from either microbial or thermogenic sources, covering a wide range of isotopic values. In these cases, the global emission-weighted δ13C value of SSs (see Sect. 5.5) was used for these regions in the δ13C grids. The global map of δ13C for SSs is shown in Fig. S5.
5.4 SS gridding
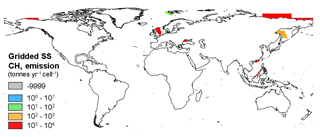
The SS grid dataset was generated digitizing polygons of the SS areas from literature maps (see references in Table S4). The final shapefile contains 31 polygons characterized by the following variables: country, longitude and latitude of the polygon centroid, CH4 output flux, area and average δ13C value of the emissions in each polygon. The value −9999 is reported for the missing emissions at 16 sites (sites 16 to 31 in Table S4). The SS layer was joined with the vector grid and the resulting map is shown in Fig. 6.
5.5 Evaluation of global SS emission and δ13C-CH4
The sum of CH4 emissions from the 15 SS areas in Table S4 (which refer to published estimates) is ∼3.9 Tg yr−1. This represents about 20 % of the theoretical estimate of global SS emission to the atmosphere (∼20 Tg yr−1), derived by process-based models, proposed by Kvenvolden et al. (2001). SS emissions also occur in the other 16 areas reported in Table S4 and likely in many other sites not investigated yet. Among the areas with missing emission values, the Gulf of Mexico and the Caspian Sea are very likely major methane emitters, followed by the northern US Atlantic margin. It is difficult to evaluate whether by adding these missing SS emissions the total sum would approach the Kvenvolden et al. estimate of 20 Tg yr−1 (however, we consider this global value as a theoretical reference for our SS gridded emission, not a target or actual value to reach). Evaluation of the SS emission factor (based on the reported area and total fluxes in Table S4) is also difficult because the areas indicated in the several works (see References in Table S4) often refer to the surveyed area and not to the actual area of seepage; in these cases, using the surveyed area would result in a strongly underestimated emission factor. However, using the relationship observed for the 15 “investigated” sites between the area (actual seepage or surveyed) and emission factor, the other 16 sites would yield total emissions of about 1 Tg yr−1. This would bring the total CH4 emission from the 15+16 sites of Table S4 to about 5 Tg yr−1. Assuming that (a) SSs generally do not take into account the release of dissolved methane (i.e. only methane bubbles are accounted for) and (b) today unknown SS areas (not listed in Table S4) may have a seepage extent that does not exceed that of the investigated areas, it is plausible that global SS emission exceeds 5 Tg yr−1. If the upper estimate for the East Siberian Arctic Shelf, 4 Tg yr−1 (Berchet et al., 2016; i.e. twice the mean used in Table S4), is considered, then the global SS emission would exceed 9 Tg yr−1. The SS emission-weighted mean value of δ13C-CH4 is −59 ‰. The non-weighted mean value is −51.2 ‰.
5.6 SS uncertainties
Spatial distribution uncertainty. In the grid, the uncertainty of the geographic distribution of the SSs is practically zero, as all seepage zones have geographic coordinates within an error <1∘.
Emission uncertainty. The main uncertainty and control on the global gridded 3.9 Tg yr−1 value is associated with the estimate of CH4 emissions from the East Siberian Arctic Shelf, for which we used the central value (2 Tg yr−1) of the range indicated by Berchet et al. (2016), i.e. 0–4 Tg yr−1 (not very dissimilar from the estimate of 2.9 Tg yr−1 suggested by Thornton et al., 2016). The other 15 SS areas, totalling ∼1 Tg yr−1, have variable uncertainty, often not defined in the individual publications. With a ±2 Tg yr−1 uncertainty for the Siberian Arctic Shelf, and arbitrarily assuming 10 % uncertainty for the other estimates, the overall SS gridded emission uncertainty would result in ±2.1 Tg yr−1 (54 %).
δ13C-CH4 uncertainty. The maximum uncertainty of the estimated δ13C values (based on criteria described in Sect. 5.3) is approximately within ±15 ‰, i.e. half of the range of δ13C values for typical microbial (−80 ‰ to −60 ‰) and thermogenic (−50 ‰ to −20 ‰) gas. The uncertainty of the emission-weighted mean (−59 ‰) is mainly controlled by emissions from the East Siberian Arctic Shelf, North Sea and Black Sea, whose δ13C values are available or estimated, ranging from −50 ‰ to −63 ‰. The overall uncertainty of the global emission-weighted mean is thus reasonably <±7 ‰.
6.1 Assessment of global MS area
The diffuse exhalation of CH4, called microseepage (MS), is widespread throughout onshore petroleum fields all over the world. It is systematically observed in correspondence with anticlines and marginal (faulted) areas of gas–oil fields (Etiope and Klusman, 2010; Tang et al., 2017). The existence of macro-seeps (OSs) in a given region also implies a high probability that MS exists in that region, even if that region falls outside a known petroleum field. Therefore, as a proxy of the activity (spatial distribution) of MS, we considered the global area of petroleum fields and a global area including OSs defined as described below. This criterion is conservative as MS may also occur in sedimentary basins without known petroleum fields and OSs (Klusman et al., 2000; Etiope and Klusman, 2010). The assessment of the global petroleum field area (PFA) and global OS area (OSA) is discussed in the Supplement (Sect. S3.1 and S3.2). The total potential MS area (PMA) resulted in PFA + OSA = 13 033 000 + 85 900 = 13 118 900 km2.
6.2 Attribution of MS levels
The level of MS CH4 emissions was established on the basis of a statistical analysis of a MS flux dataset (see Sect. 6.2.1) and considering the theory of seepage migration mechanisms, for which the gas flux greatly depends on the permeability of the rocks, especially when induced by faults and fracture networks (Etiope and Klusman, 2010; Etiope, 2015; Tang et al., 2017). Accordingly, the attribution of the flux within the PMA (PFA + OSA) was done considering the presence/absence, in each cell, of three major geological factors, which are proxies of methane seepage and gas permeability, i.e. OSs, faults and seismicity, as explained in Sect. 6.2.2.
6.2.1 Statistics of MS data
A dataset of 1509 MS CH4 flux measurements was compiled based on available literature and unpublished works. The data are from 19 petroleum areas: 8 in the USA (Klusman et al., 2000; Klusman, 2003, 2005; Klusman, unpublished; LT Environmental, 2007), 6 in Italy (Etiope and Klusman, 2010; Sciarra et al., 2013; Etiope, 2005; Etiope, unpublished), 1 in Romania (Etiope, 2005), 1 in Greece (Etiope et al., 2006; Etiope, unpublished) and 3 in China (Tang et al., 2007, 2010, 2017). The resulting descriptive statistics are reported in Table S5.
The data are divided into two groups: (a) negative and near-zero values (<0.01 mg m−2 d−1, considering minimum analytical error), which represent the normal CH4 flux in dry (not flooded) soils, and (b) positive values (>0.01 mg m−2 d−1; i.e. microseepage). The similar order of magnitude between the median and the geometric mean flux indicates a log-normal behaviour of the positive CH4 flux distribution. The positive values represent about 57 % of total measurements. This implies that MS does not occur throughout the entire PFA. This is well known, as CH4 flux from the ground, in addition to underground rock permeability and fluid pressures, also depends on soil conditions (humidity, porosity, temperature) and methanotrophic activity. Accordingly, and taking into account that the MS measured sites are geographically dispersed with a relatively homogeneous spatial distribution (and the measurements were taken in different seasons), we reduced the PFA by removing 43 % of the area as described in Sect. 6.4. A new MS area was therefore defined as the effective microseepage area (EMA), which is OSA + 57 % of PFA. The derivation of the EMA area is described in Sect. 6.4. A frequency histogram and normal probability plot (NPP) of MS data (logarithmic positive values) confirm that flux values have a log-normal distribution (Fig. S7). Values exceeding 1000 mg m−2 d−1 (up to 7078) were excluded as they represent special and rare cases of MS (often not distinguishable from miniseepage, which is the halo surrounding macro-seeps).
The combined analysis of the NPP and frequency histogram (Fig. S7) resulted in the identification of four main groups of positive flux data, i.e. four levels of MS:
-
Level 1 0.01–12 (median: 1.3) mg m−2 d−1
-
Level 2 12–60 (median: 31.1)
-
Level 3 60–300 (median: 110)
-
Level 4 300–1000 (median: 493.5)
Level 0 implies the absence of MS. The median of each level was assigned to the grid cells included in the area with expected MS defined in Sect. 6.2.2 and according to the presence of the factors influencing MS. The median was chosen because it is not affected by outliers within each level, providing conservative flux values.
6.2.2 Factors influencing MS level: presence of macro-seeps, faults and seismicity.
The four MS levels (1, 2, 3 and 4) are associated with four different combinations of the three factors influencing the gas flux, following MS theory and experimental data.
- a.
Fault data were taken from 17 different datasets (see sources of databases in the Supplement): the main one is the Global Faults layer of ArcAtlas (Finko, 2014). It includes two types of faults: (1) faults created by the dislocation of rocks that define the geological structures of the continents (tectonic contacts and thrust-faults) and (2) faults created by the morphology of the present-day relief and morphostructure (steps and rifts). The first type of faults refers to ancient structures, while those revealed by relief are comparatively young structures that appeared during the neotectonic stage of the Earth's evolution (mostly in the Neogene and Quaternary periods). The other 16 fault datasets are national or regional datasets from Afghanistan, Australia, Bangladesh, the Caribbean region, central Asia, Europe including Turkey, Georgia, Greece, Ireland and Italy, New Zealand, South America, the southern Mediterranean area, Spain, Switzerland and UK (see Supplement). The final merged fault dataset includes 156 095 tectonic elements (Fig. S8); obviously it does not include all actual existing faults on Earth. The dataset must be interpreted as a global distribution of the main regional fault systems and fractured zones.
- b.
The epicentres of earthquakes are proxies of fault location and activity (permeability), so they also represent the presence of active faults, which may not be reported in the fault dataset. It is also known that gas migration and escape to the surface may increase with seismic activity. We used the seismicity dataset of USGS Earthquake Lists, Maps and Statistics (see sources of databases in the Supplement). We extracted only onshore seismic events with magnitude M > 4.5 recorded from 2005 to 2017. This resulted in a dataset of 18 157 onshore epicentres covering 177 countries (Fig. S9).
- c.
The presence of macro-seeps (OSs) are themselves an expression of regional seepage activity. The OS area is described in the Supplement (Sect. S3.2).
The three factors, faults, seismicity and presence of seeps, were applied on the gridded EMA as described in Sect. 6.4.
6.3 Attribution of the δ13C value
Measured and published data of δ13C-CH4 in gas MS are scarce and only available for a few petroleum fields. However, during the seepage process (migration driven by pressure gradients, i.e. advection), the CH4 isotopic composition does not change significantly, so that surface CH4 flux basically has the same δ13C value of the original gas in the reservoir (e.g. Etiope et al., 2009). Therefore, for each field or basin, the MS δ13C value was taken from published data related to subsurface reservoirs. A limitation of this strategy is that in a given basin the MS gas may actually come from shallower reservoirs, not necessarily or not dominantly from the deep productive reservoirs, which are more frequently the literature source of the isotopic value. Therefore, in some cells the real isotopic value could be lighter than that used in the grid maps.
Accordingly we adopted the following procedure:
-
When one or more seeps (OSs) occur in a petroleum field (in the “Petrodata” list), the average δ13C-CH4 of those seeps was used for MS.
-
In the absence of seeps, reservoir δ13C-CH4 data were used; they were taken from the inventory described by Sherwood et al. (2017) or published literature. For the fields (in the Petrodata list) whose δ13C-CH4 value is not reported either in Sherwood et al. (2017) or literature, a theoretical δ13C-CH4 value was estimated on the basis of the type of gas (microbial or thermogenic) and maturity of the petroleum system.
The file contains 349 δ13C-CH4 data points (from 891 petroleum fields). It was not possible to estimate a specific δ13C value for the remaining 542 petroleum fields. In these cases, the global emission-weighted isotopic value was used in the resulting empty cells, as described in Sect. 6.4.
6.4 MS gridding
PFA and OSA (described in the Supplement) were intersected with a high-resolution () global grid. The cell dimension corresponds to the maximum resolution that can be obtained using ArcGIS software (the software cannot handle shapefiles >2 GB). The high-resolution gridding was used to match, as much as possible, the PFA: gridded PFA is in fact 14 791 897 km2, while the original PFA was 13 033 750 km2. The high-resolution gridding also served to reduce the boundary effect, and thus the overestimation of the areas with MS enhancing factors, i.e. faults, earthquake and seeps (the larger the cells, the higher the probability that the cells include MS enhancing factors).
As discussed in Sect. 6.2.1, only 57 % of PFA cells were considered to host MS. It was then necessary to delete 43 % of PFA cells. The cells were randomly deleted only among those that do not host MS enhancing factors (faults, earthquakes and seeps), i.e. empty cells (which are 93 % of total PFA). The overall PFA reduction of 43 % was obtained by deleting 54 % of the empty cells (resulting in a PFA of 8 408 360 km2). Combining PFA and OSA results in EMA (Table S6). The sequence of MS modelling is summarized in the block diagram of Fig. S10. The MS levels were then assigned to the gridded EMA according to the presence of the factors influencing MS: (a) the presence of faults, (b) the presence of seismic activity and (c) the presence of macro-seeps (OSs), as follows.
-
Level 1 was applied to cells without any geological factors.
-
Level 2 was applied to cells with faults or earthquakes.
-
Level 3 was applied to cells with faults plus earthquakes or oil seeps or gas-bearing springs.
-
Level 4 is applied to cells with gas-seeps or mud volcanoes.
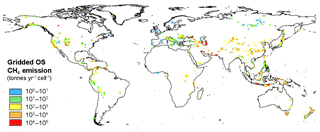
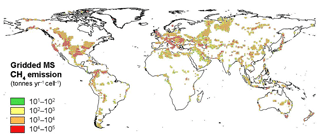
The resulting global MS CH4 emissions are about 24 Tg yr−1. The emissions per cell range from 14.7 t yr−1 (cells of about 30 km2) to 29 446 t yr−1 (cells of about 169 km2). The grid was then converted into resolution for atmospheric modelling applications (Fig. 7). MS emissions occur in 3039 cells, ranging from 15 to 471 000 t yr−1. The cell with the highest emission is located in the Caspian region (Azerbaijan). The sensitivity of the MS modelling is discussed in the Supplement (Sect. S3.3).
6.5 Evaluation of global MS emission and δ13C-CH4
The global MS emission derivable by summing the emission from the cells of the four MS classes, about 24 Tg yr−1 (Table S6), is within the range, 10–25 Tg yr−1, previously suggested by Etiope and Klusman (2010). The emission-weighted δ13C-CH4 resulting from gridded MS is −51.4 ‰ (non-weighted average is −46.4 ‰). This value is mostly influenced by areas with elevated MS of microbial gas, such as the Po Basin (Italy), the Transylvanian Basin (Romania) and the Powder River basin (USA). The global emission-weighted value was applied to cells without isotopic values.
6.6 MS uncertainties
Spatial distribution uncertainty. The uncertainty of the spatial distribution of MS depends on the assumption, supported by field measurements, that MS occurs significantly only within petroleum fields (PFA) and areas with seeps (OSA). The uncertainty of PFA depends on the Petrodata dataset of Päivi et al. (2007), discussed in Sect. 5.1, and it cannot be quantified. The uncertainty of OSA depends on the buffer applied to individual seeps, which was however defined by geospatial analysis (see Sect. S3.2).
Emission uncertainty. The uncertainty of the MS emission depends on the activity (EMA) and on the process-based model of attribution of the seepage levels (emission factors), and their statistical elaboration, discussed in Sect. 6.2 (see also Fig. S10). Changing activity by ±20 % and the emission factor by the 95 % confidence interval of the median, with different combinations, resulted in a total MS output ranging from 15 to 32.7 Tg yr−1, with a mean of 23 Tg yr−1, matching the first estimate (see Supplement). We can therefore set, approximately, a maximum uncertainty in the total MS output of ±9 Tg yr−1 (about ±38 %).
The model was then tested comparing its output values with measured values. This comparison was possible for nine areas where the coordinates of the measurement points were identified. In all cases, measured and modelled values have the same order of magnitude, and in many cases the range of the MS level attributed by the model includes the mean value measured.
δ13C uncertainty. The uncertainty of individual MS δ13C values depends on the assumptions discussed in Sect. 6.3. The uncertainty of the emission-weighted mean (−51.4 ‰) is mainly controlled by the cells with larger MS emissions where δ13C values are estimated. When the cells with emission-weighted mean are excluded, the remaining 536 cells (at , over a total of 192 166) have emission ranging from 5623 to 8296 t yr−1 and δ13C values from −65 ‰ to −35 ‰ (mean −53.4 ‰). The difference of this value with the emission-weighted mean, i.e. 2 ‰, may be considered as approximate expression of the uncertainty of the global emission-weighted mean.
7.1 Global GM distribution
The global distribution of CH4-emitting geothermal–volcanic sites (GMs) generated here is based on an inventory of volcanoes and geothermal sites developed by the Global Volcanism Program (2013) (see sources of databases in the Supplement). This inventory reports all major volcanic–geothermal systems on Earth (2378 sites; Fig. S12). They include both Holocene systems (1307 sites distributed in 128 countries), and older, Pleistocene volcanic systems (1071 sites distributed in 119 countries), which represent geothermal areas. In order to convert the point data into more realistic areal data (polygons), an arbitrary buffer area of 4 km of radius was created for each GM point (the buffer area does not influence the overall emission estimate, being only a parameter guiding the gridding). It is important to outline that this inventory reports the “zones” of volcanic–geothermal sites, and does not list individual manifestations: for example, the numerous geothermal manifestations in central Italy are cumulatively included in a few lines, e.g. “Vulsini complex”, “Sabatini complex” and “Vulture”. Therefore each emission value, attributed as explained in Sect. 7.2, represents a “regional” GM emission.
7.2 Attribution of CH4 emission levels
Methane flux measurements and regional total estimates in GMs are available only in a few cases (<100 sites), mostly in Europe (as reviewed by Etiope et al., 2007). The GM inventory refers to geothermal–volcanic areas where GMs are expected to occur, but their actual surface area is unknown. Therefore, even assuming an emission factor (from the limited flux dataset), it cannot be translated into emission for each GM site. In this work, theoretical numbers were adopted considering three classes of regional emissions: 500, 5000 and 10 000 t yr−1, as central values of the ranges 100–1000, 1000–10 000 and 5000–15 000 t yr−1, respectively. These ranges were derived from emission factors ranging from 1 to 150 t km−2 yr−1 (Etiope et al., 2007) applied on an area of 100 km2, as an average order of magnitude of the extension of geothermal–volcanic zones (derived from the Global Volcanism Program, 2013). Although the GM emission grid developed here is expected to improve global CH4 inverse modelling (as it includes previously neglected GM sources), the total GM emission estimate suggested by the gridding because of the uncertainty of the theoretical emissions, is not meant to update or refine the previous global GM emission estimate (derived by process-based modelling; Etiope, 2015).
The emission level was attributed based on
- a.
the location of the geothermal site, which may be within or outside a sedimentary basin (Fig. S13);
- b.
the concentration of CH4 measured in the geothermal fluids, within and outside a sedimentary basin.
The amount of methane in a geothermal–volcano area depends, in fact, on the presence of sediments rich in organic matter, which may be a source of thermogenic gas in addition to the geothermal abiotic gas. The CO2 ∕ CH4 ratio of emissions to the atmosphere is in the order of 1000–10 000 in volcanic sites, with limited sedimentary contribution, and it ranges from 1 to 100 in geothermal systems characterized by important sedimentary covers. Sediment-hosted geothermal systems in sedimentary basins (e.g. Etiope, 2015; Mazzini and Etiope, 2017) show the highest CH4 concentrations (lowest CO2 ∕ CH4 ratio). In addition, sedimentary basins hosting petroleum fields reasonably contain larger amounts of methane. The three classes of methane emissions are reported in Table S9.
7.3 Attribution of the δ13C value
A specific dataset was compiled listing 98 published δ13C-CH4 values of various, geographically dispersed, geothermal–volcanic systems in the world. The isotopic δ13C-CH4 values range from −43.2 ‰ to −6.4 ‰, with an average of −26.7 ‰. The double-sided Grubbs test (Grubbs, 1969) identified four outliers; the mean δ13C-CH4 value of the 94 values excluding the outliers is −26.5 ‰. It is known that geothermal methane in sedimentary basins, due to the presence of organic matter and related thermogenic gas, has a lower δ13C-CH4 value compared to magmatic, sediment-free systems (e.g. Welhan, 1988). The NPP of the δ13C-CH4 data shows a sharp deviation at about −29 ‰ (Fig. S14). This value is actually consistent with the isotopic boundary of dominantly thermogenic gas; we therefore used this value as the limit between GMs falling outside sedimentary basins and GMs within sedimentary basins. The mean values of the two classes (excluding the outliers) are summarized in Table S8.
7.4 GM gridding
The GM shapefile generated in an ArcGIS environment was spatially joined to the vector square grid. The result is reported in Table S9 and mapped in Fig. 8.
7.5 Evaluation of global GM emission and δ13C-CH4
The 2378 GM sites yield a total methane emission of about 5.7 Tg yr−1, which is within the range of the latest global GM emission estimate (2.2–7.3 Tg yr−1; Etiope, 2015). The emission-weighted mean value of δ13C-CH4 for the GM emission is −30.6 ‰ (non-weighted mean is −27.5 ‰).
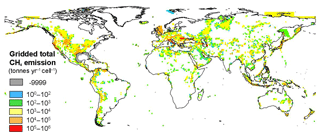
Figure 9Gridded map of total methane emission from OSs + SSs + MS + GMs. This map refers to the csv file “Total geoCH4_output_2018”.
Table 3Global gridded, global extrapolated and global published geo-CH4 emissions.
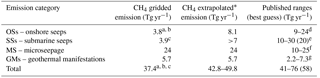
* Including estimates from notes a, b and c. See also text below. a Not including MV eruptions. b Partial (estimated <50 %) gas–oil seeps emissions. c Excluding unidentified or not-investigated offshore seepage sites. d Etiope et al. (2008); Etiope et al. (2011) (see also Table 3). e Kvenvolden et al. (2001). f Etiope and Klusman (2010). g Etiope (2015).
7.6 GM uncertainties
Spatial distribution uncertainty. The uncertainty of the spatial distribution of GMs has the same uncertainty as the global distribution of geothermal–volcanic areas, derived from the Global Volcanism Program (2013).
Emission uncertainty. The gridded GM emission, equivalent to the sum of individual regional values attributed as described in Sect. 7.2, has an uncertainty of about 75 % (5.7±4.3 Tg yr−1).
δ13C uncertainty. The uncertainty of emission-weighted GMs δ13C may refer to the average of the two values corresponding to the 95 % confidence interval of the means of the two groups of isotopic data (outside and within sedimentary basins) discussed in Sect. 6.3, i.e. ±2.5 ‰.
8.1 Global geo-CH4 emission
The global geo-CH4 emission distribution, obtained merging OS, SS, MS and GM grids, is shown in Fig. 9. The total gridded CH4 emission is 37.4 Tg yr−1 (Table 3, second column). The extrapolated gridded emission estimate including the factors not considered in the gridding procedure (i.e. mud volcano eruptions, existence of onshore and offshore seeps not included in the OS–SS inventories) is between about 43 and 50 Tg yr−1 (Table 3, third column). These values are within the published global bottom-up estimates (Table 3, fourth column). The global extrapolated geo-CH4 emission is then compatible with recent top-down estimates (about 50 Tg yr−1 by Schwietzke et al., 2016; see also Sect. 9 for a wider discussion addressing the temporal variability of geological methane emissions). The scope of columns 3 and 4 in Table 3 (extrapolated and published emission estimates) is only to show that gridded emissions do not necessarily represent the actual global geo-CH4 emission because the datasets developed for the gridding may not be complete or may not contain the information necessary for improving previous estimates. Considering the four geo-CH4 source categories individually, the gridded MS and GM emission totals are, however, within published ranges. The differences between gridded and published OSs and SSs are largely due to the following:
-
an incomplete OS dataset (it represents only 30 % of global number of seeps assumed to exist on Earth);
-
a lower estimate of the global MV area (680 km2 instead of 2800 km2 assumed in previous works);
-
an incomplete SS flux dataset (flux data missing from at least 16 areas with known gas emissions).
The gridded emissions may only represent an updated assessment of the global emissions for MS and MVs (part of OSs) because the gridding implied a careful assessment of the spatial distribution and emission factors for these types of geo-sources.
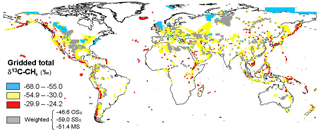
8.2 Global geo-CH4 δ13C
Based on the emission-weighted δ13C value for each category of emission (using the respective emissions from Table 3), the global geo-CH4 emission-weighted average δ13C is −49.4 ‰, considering global emission estimates and −48.5 ‰ for gridded emissions (Table 4). The global distribution of the isotopic signature is shown in Fig. 10.
8.3 Uncertainties of gridded geo-CH4 distribution, emission and isotopic values
The overall uncertainties of the spatial distribution of the geo-CH4 sources, CH4 emissions and emission-weighted average values of δ13C, depend on individual uncertainties of the four categories of seepage, as discussed in Sects. 4.6, 5.6, 6.6 and 7.6. These are summarized in Table 5.
The fluxes of natural gas seepage from the Earth's crust are not constant, either on short (hours, days, months, seasons) or long (years, centuries, millennia) timescales. Seepage variations can be induced by endogenous (geological) and exogenous (atmospheric) factors, including subsurface gas pressure variations (controlled mainly by gas migration and accumulation processes), changes of fracture permeability (tectonic stress, seismicity), hydrostatic aquifer variations and meteorological and climatic changes (atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity and microbiological activity in the soil; Etiope, 2015). Mud volcano episodic eruptions (Mazzini and Etiope, 2017), seismicity-related degassing (e.g. Manga et al., 2009) and seasonal variability of microseepage (higher in winter due to lower methanotrophic consumption in the soil; Etiope and Klusman, 2010), are three well studied examples of geo-CH4 emission variability. Anthropogenic activity, through modification of aquifer pressures (water pumping) and petroleum exploitation (with consequent decrease of reservoir pressures) can also induce seepage variability over time (e.g. Etiope, 2015). Therefore the global geo-CH4 emission reported in this work, as well as in all other estimates available in the literature, must be interpreted as average, present-day degassing. Substantial decadal changes of seepage could occur as a result of decadal changes of hydrostatic aquifer pressure (e.g. Famiglietti, 2014) and decadal changes of seismicity (e.g. Mogi, 1979). Specific empirical studies are however missing, and with the present state of knowledge it is impossible to provide a temporal variability factor.
Table 6Combinations of bottom-up and top-down estimates of geological methane emissions (Tg yr−1).
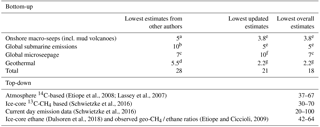
a Dimitrov (2003). b Kvenvolden et al. (2001). c Klusman et al. (1998). d Lacroix (1993). e This work. f Etiope and Klusman (2010). g Etiope (2015).
On longer, geological timescales, a series of proxies suggested that geo-CH4 emissions could have been quite variable over the Quaternary period (Etiope et al., 2008b). Recent estimates on geo-CH4 emission at the end of the Pleistocene deserve a specific discussion. Based on radiocarbon (14C) measurements in methane trapped in ice cores in Antarctica, Petrenko et al. (2017) estimated the absolute amount of 14C-containing CH4 in the atmosphere 11–12 000 years ago, between the Younger Dryas and Preboreal intervals; this allowed them to estimate that the maximum global natural, geological (14C-free) CH4 emission for that period was at most 15.4 Tg yr−1. More recent analyses by the same authors confirmed this value (Dyonisius et al., 2018). These authors then assumed that past geological methane emissions were no lower than today. They concluded, therefore, that present-day geological CH4 emissions are much lower than present-day bottom-up estimates (54–60 Tg CH4 yr−1; Etiope, 2015; Ciais et al., 2013). Without entering discussions on the accuracy and meaning of the ice core 14C-based analyses and their temporal extrapolation to today, the following investigates whether the estimate by Petrenko et al. (2017) is compatible with
- a.
the estimates provided by authors other than Etiope (2015) and those reported in the present gridding work,
- b.
the lowest bottom-up geo-CH4 emission estimates available so far,
- c.
present-day top-down geo-CH4 emission estimates derived by different techniques, and
- d.
pre-industrial geo-CH4 emission estimates based on ice-core ethane measurements and observed geo-CH4 / ethane ratios.
Table 6 summarizes the data including individual literature references. In the bottom-up estimate table, the third column reports the lowest estimates proposed on the basis of more recent datasets and emission factors, which are updated in comparison with the earlier estimates (reported in the second column). The last column reports the overall lowest estimates, from old and new works, i.e. the minimum emission values derivable from different extrapolations. This comparison shows that the Petrenko et al. (2017) estimate is lower than any bottom-up estimate, regardless of authorship. The top-down estimate table reports geo-CH4 emission derivable by three different procedures:
- a.
The portion of 14C-free CH4 in the present-day atmosphere is assessed (i.e. 30 %; Lassey et al., 2007), then the equivalent 14C-free CH4 emission is calculated (30 % of total CH4 emission, ∼558 Tg yr−1, i.e. 167 Tg yr−1; Saunois et al., 2016) and the anthropogenic 14C-free component is subtracted (fossil fuel fugitive emissions from inventories ∼100–130 Tg yr−1; EDGARv4.2; Saunois et al., 2016). The natural component (geo-CH4 emission) would be 37–67 Tg yr−1.
- b.
Methane concentration and isotopic data from ice-core records are used, based on box modelling by Schwietzke et al. (2016), suggest a geo-CH4 emission of 30–70 (50) Tg yr−1.
- c.
With the same box model plus 3-D forward modelling, but using a present-day atmospheric methane and isotopic data, Schwietzke et al. (2016) suggested a present-day total fossil fuel (oil–gas–coal industries plus geological) CH4 emission of 150–200 Tg yr−1. Considering that oil–gas–coal emission inventories indicate 100–130 Tg yr−1, geo-CH4 emission could be 20–100 Tg yr−1, consistent with approach (b) but with a wide uncertainty range.
- d.
Using ethane concentration data from ice-core records, the 3 Tg yr−1 ethane top-down estimates by Dalsoren et al. (2018) confirm earlier bottom-up estimates of 2–4 Tg yr−1 ethane (Etiope and Ciccioli, 2009). Observed geo-CH4 / ethane emission ratios would then suggest 42–64 Tg CH4 yr−1.
Overall, geo-CH4 emissions derived by top-down estimates range between 20 and 100 Tg yr−1. These values are consistent with bottom-up estimates but substantially higher than the Petrenko et al. (2017) estimate. The following options should then be considered:
- i.
All present-day bottom-up and top-down geo-CH4 emission estimates are biased high.
- ii.
The Petrenko et al. (2017) estimate is biased low.
- iii.
All estimates are reasonable, but the assumption that past Younger Dryas to Preboreal geo-CH4 emissions were not lower than today does not hold.
The free availability of the data does not constitute permission for their publication. If the data are essential to new modelling, or to develop results and conclusions of a paper, co-authorship may need to be considered. Grid csv files (emission and isotopic composition for each geological source and integrated grid files) and microseepage and geothermal manifestation inventories are available at https://doi.org/10.25925/4j3f-he27 (Etiope et al., 2018), including full contact details and information on how to cite the data. The SS inventory is provided in the Supplement (Table S4). Due to CGG (2015) license restrictions, the OS inventory can be requested at https://www.cgg.com/en/What-We-Do/Multi-Client-Data/Geological/Robertson-Geochemistry.
The datasets of petroleum fields, faults, volcanic–geothermal sites, earthquakes and sedimentary basins are available on the web as described in the Supplement.
Gridded maps of global geological CH4 emissions at resolution have been developed comprehensively for the first time for atmospheric modelling and evaluation of global CH4 sources. The maps, elaborated by ArcGIS and provided as csv files, include the four main categories of natural geological CH4 emissions: onshore hydrocarbon seeps (OSs), submarine (offshore) seeps (SSs), diffuse microseepage (MS) and geothermal manifestations (GMs). A combination of published and originally ad hoc developed datasets was used to determine the emission factors and the areal distribution and extent (activity) of the several geo-CH4 sources and their stable carbon isotope signature (δ13C). Due to the limited number of direct CH4 flux measurements, globally and regionally representative CH4 emission factors for OSs, MS and GMs were estimated based on experimental emission factors (measurements) and statistical approaches. Methane emission estimates for SSs were adopted directly from published regional emission estimates. The results of this work can be summarized as follows:
- a.
The global geo-CH4 source map reveals that the regions with the highest CH4 emissions are all located in the Northern Hemisphere, in North America, in the Caspian region, in Europe and in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf.
- b.
The globally gridded CH4 emission estimate (37.4±17.6 Tg yr−1, exclusively based on data and modelling specifically targeted for gridding, and 43–50 Tg yr−1 when extrapolated to also account for onshore and submarine seeps with no location specific measurements available) is compatible with published ranges derived by top-down and bottom-up procedures.
- c.
The procedures adopted to attribute CH4 fluxes to mud volcanoes (MVs, an OS sub-class) and microseepage (MS) are based on a detailed assessment of the activity (areas) and emission factors, and the resulting gridded total output can be considered a refinement of previously published emission estimates. Specifically, the global MV emission estimate (2.8 Tg yr−1, excluding eruptions) is compatible with early estimates by Dimitrov (2002), Milkov et al. (2003), Etiope and Milkov (2004) and Etiope et al. (2008). Global MS emissions (previously estimated between 10 and 25 Tg yr−1; Etiope and Klusman, 2010) are now estimated to be Tg yr−1.
- d.
Regional emissions of SSs are available from the literature for only a limited number of cases. The regions with missing emission data in the literature are not included in the gridded dataset developed here. As a result, the gridded CH4 emission estimate (3.9 Tg yr−1) is substantially smaller than a previously published global total estimate (20 Tg yr−1, which would include extrapolated values to regions without region-specific estimates (Kvenvolden et al., 2001). However, the published SS estimate has large uncertainties (at least 10 Tg CH4 yr−1, since two separate estimates of 10 and 30 Tg CH4 yr−1 were actually provided without indication of their uncertainties) and it was purely based on process-based modelling (Kvenvolden et al., 2001). This work verified that SS emissions also occur in other regions where emission values are missing (among these, the Gulf of Mexico, the Caspian Sea and the northern US Atlantic margin). Given an estimated SS emission factor, we propose that global SS CH4 emissions may range between 5 and 12 Tg yr−1, with a best guess (central value) of 8.5 Tg yr−1.
- e.
The emission-weighted global mean of δ13C-CH4 is −48.5 ‰ for the gridded emissions, and −49.4 ‰ when gridded OS and SS emissions are extrapolated to include all global regions. The second value is therefore more realistic. Both values are significantly lower (about 4 ‰–5 ‰ lighter) than typical values attributed to fossil fuel industry sources (−44 ‰ by Schwietzke et al., 2016) and much lower (10 ‰–11 ‰ lighter) than seepage values considered in inverse studies (−38 ‰ by Sapart et al., 2012). Clearly, natural geological sources are more 13C-depleted than generally assumed (and this mostly occurs as microseepage and submarine seepage). Low maturity thermogenic gas and microbial gas are, in fact, a neglected, but considerable, fraction of the global fossil CH4 budget (Sherwood et al., 2017). It is expected that using the updated, more 13C-depleted, isotopic signatures in atmospheric modelling studies will increase the top-down estimate of the global geological CH4 sources (all else equal).
The maps developed here represent important inputs for future atmospheric modelling of the global CH4 cycle. Fossil fuel industry “upstream” activities (exploration, production and some processing of fossil fuels) and associated CH4 emissions occur largely on the land surface above sedimentary basins that are also the habitat for geological CH4 seepage. Thus, there is substantial spatial overlap in CH4 emissions from the fossil fuel industry and geological seepage. Nevertheless, there is substantial spatial variability in CH4 emission intensity for both the fossil fuel industry (Maasakkers et al., 2016; JRC/PBL, 2017) and geological seepage (this work). In the absence of a comprehensive gridded geological CH4 seepage product, global or regional inverse model studies would erroneously attribute a low bias to CH4 emissions from geological seepage. This is because of a de facto zero geological a priori estimate. At the same time, the inverse studies would erroneously attribute a high bias to CH4 emissions from fossil fuel industry activity (and potentially other sources) while correctly reporting total emissions of all sources. The geological seepage data and maps developed here can be used to refine fossil fuel industry and microbial CH4 emission budgets at the regional and global level. Finally, methane / ethane and methane / propane source composition ratios are available for the four categories of geo-sources (preliminary data were used in Etiope and Ciccioli, 2009) for use beyond the scope of this work. Combining the gridded geo-CH4 emissions and the available source composition data, gridded ethane and propane maps could be developed in the future. The gridded geo-CH4 maps shall be updated when additional, statistically significant gas flux data for the several seepage categories become available. Geo-CH4 emission from a fifth, recently discovered, geological category, the seepage from serpentinized peridotites (e.g. Etiope and Schoell, 2014; Etiope et al., 2017 and references therein) shall also be gridded when sufficient flux data become available.
The supplement related to this article is available online at: https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-11-1-2019-supplement.
GE and SS conceived the geological methane emission gridding project. GE and GC carried out gridding and mapping. All authors reviewed the data and contributed to the paper writing.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
The work was supported by NASA grant NNX17AK20G. Thanks
are due to Lori Bruhwiler for revising an early version of the manuscript
and to three anonymous reviewers.
Edited by: Attila Demény
Reviewed by: three anonymous referees
Aliyev, A. A., Guliyev, I. S., and Feyzullayev, A. A.: What do we know about mud volcanoes Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences Geology Institute, Qoliaf qrup QSC, Baku, 206 pp., 2012.
Berchet, A., Bousquet, P., Pison, I., Locatelli, R., Chevallier, F., Paris, J.-D., Dlugokencky, E. J., Laurila, T., Hatakka, J., Viisanen, Y., Worthy, D. E. J., Nisbet, E., Fisher, R., France, J., Lowry, D., Ivakhov, V., and Hermansen, O.: Atmospheric constraints on the methane emissions from the East Siberian Shelf, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 16, 4147–4157, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-4147-2016, 2016.
Bergamaschi, P., Houweling, S., Segers, A., Krol, M., Frankenberg, C., Scheepmaker, R. A., Dlugokencky, E., Wofsy, S. C., Kort, E. A., Sweeney, C., Schuck, T., Brenninkmeijer, C., Chen, H., Beck, V., and Gerbig, C.: Atmospheric CH4 in the first decade of the 21st century: Inverse modeling analysis using SCIAMACHY satellite retrievals and NOAA surface measurements, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 118, 7350–7369, https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50480, 2013.
Bousquet, P., Ciais, P., Miller, J. B., Dlugokencky, E. J., Hauglustaine, D. A., Prigent, C., Van der Werf, G. R., Peylin, P., Brunke, E. G., Carouge, C., Langenfelds, R. L., Lathiere, J., Papa, F., Ramonet, M., Schmidt, M., Steele, L. P., Tyler, S. C., and White, J.: Contribution of anthropogenic and natural sources to atmospheric methane variability, Nature, 443, 439–443, 2006.
CGG: Organic Geochemistry Data from FRogi and Fluid Features Database, available at: https://www.cgg.com/en/What-We-Do/Multi-Client-Data/Geological/Robertson-Geochemistry (last access: 30 November 2018), 2015.
Ciais, P., Sabine, C., Bala, G., Bopp, L., Brovkin, V., Canadell, J., Chhabra, A., DeFries, R., Galloway, J., Heimann, M., Jones, C., Le Quéré, C., Myneni, R. B., Piao, S., and Thornton, P.: Carbon and Other Biogeochemical Cycles, in: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of IPCC, edited by: Stocker, T. F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S. K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., and Midgley, P. M., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2013.
Clarke, R. H. and Cleverly R. W.: Leakage and post-accumulation migration, in: Petroleum migration, edited by: England, W. A. and Fleet, A. J., Geol. Soc. Sp., London, 59, 265–271, 1991.
Dalsøren, S. B., Myhre, G., Hodnebrog, Ø., Myhre, C. L., Stohl, A., Pisso, I., Schwietzke, S., Höglund-Isaksson, L., Helmig, D., Reimann, S., Sauvage, S., Schmidbauer, N., Read, K. A., Carpenter, J. J., Lewis, A. C., Punjabi, S., and Wallasch, M.: Discrepancy between simulated and observed ethane and propane levels explained by underestimated fossil emissions, Nat. Geosci., 11, 178–184, 2018.
Dimitrov, L.: Mud volcanoes – the most important pathway for degassing deeply buried sediments, Earth-Sci. Rev., 59, 49–76, 2002.
Dimitrov, L.: Mud volcanoes – a significant source of atmospheric methane, Geo-Mar. Lett., 23, 155–161, 2003.
Dyonisius, M., Petrenko, V. V., Smith, A. M., Beck, J., Schmitt, J., Menking, J. A., Shackleton, S. A., Hmiel, B., Vimont, I., Hua, Q., Yang, B., Seth, B., Bock, M., Beaudette, R., Harth, C. M., Baggenstos, D., Bauska, T. K., Rhodes, R., Brook, E., Fischer, H., Severinghaus, J. P., and Weiss, R. F.: The contribution of geologic emissions, thawing permafrost and methane hydrates to the global methane budget – perspective from ice core records, AGU Fall Meeting 2018, Abstract, 2018.
EDGARv4.2: European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC)/Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (PBL), Emission Databse for Global Atmospheric Research (EDGAR), release version 4.2, available at: http://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu (last access: 30 November 2018), 2011.
Etiope, G.: Mud volcanoes and microseepage: the forgotten geophysical components of atmospheric methane budget, Ann. Geophys., 48, 1–7, 2005.
Etiope, G.: Methane uncovered, Nat. Geosci., 5, 373–374, 2012.
Etiope, G.: Natural Gas Seepage, The Earth's hydrocarbon degassing, Springer, Switzerland, 199 pp., 2015.
Etiope, G.: Natural Gas, Encyclopedia of Geochemistry, Earth Sciences Series, Springer, Switzerland, 1–5, 2017.
Etiope, G. and Klusman, R. W.: Geologic emissions of methane to the atmosphere, Chemosphere, 49, 777–789, 2002.
Etiope, G. and Milkov, A. V.: A new estimate of global methane flux from onshore and shallow submarine mud volcanoes to the atmosphere, Environ. Geol., 46, 997–1002, 2004.
Etiope, G. and Ciccioli, P.: Earth's degassing – A missing ethane and propane source, Science, 323, p. 468, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1165904, 2009.
Etiope, G. and Klusman, R. W.: Microseepage in drylands: flux and implications in the global atmospheric source/sink budget of methane, Global. Planet. Change, 72, 265–274, 2010.
Etiope, G. and Sherwood Lollar, B.: Abiotic methane on Earth, Rev. Geophys., 51, 276–299, 2013.
Etiope, G. and Schoell, M.: Abiotic gas: atypical but not rare, Elements, 10, 291–296, 2014.
Etiope, G., Papatheodorou, G., Christodoulou, D., Ferentinos, G., Sokos, E., and Favali P.: Methane and hydrogen sulfide seepage in the NW Peloponnesus petroliferous basin (Greece): origin and geohazard, Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull., 90, 701–713, 2006.
Etiope, G., Fridriksson, T., Italiano, F., Winiwarter, W., and Theloke, J.: Natural emissions of methane from geothermal and volcanic sources in Europe, J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res., 165, 76–86, 2007.
Etiope, G., Lassey, K. R., Klusman, R. W., and Boschi, E.: Reappraisal of the fossil methane budget and related emission from geologic sources, Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L09307, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL033623, 2008a.
Etiope, G., Milkov, A. V., and Derbyshire, E.: Did geologic emissions of methane play any role in Quaternary climate change?, Global Planet. Change, 61, 79–88, 2008b.
Etiope, G., Feyzullayev, A., and Baciu, C. L.: Terrestrial methane seeps and mud volcanoes: a global perspective of gas origin, Mar. Petrol. Geol., 26, 333–344, 2009.
Etiope, G., Nakada, R., Tanaka, K., and Yoshida, N.: Gas seepage from Tokamachi mud volcanoes, onshore Niigata Basin (Japan): origin, post-genetic alterations and CH4-CO2 fluxes, Appl. Geochem., 26, 348–359, 2011.
Etiope, G., Samardžić, N., Grassa, F., Hrvatović, H., Miošić, N., and Skopljak, F.: Methane and hydrogen in hyperalkaline groundwaters of the serpentinized Dinaride ophiolite belt, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Appl. Geochem., 84, 286–296, 2017.
Etiope, G., Ciotoli, G., Schwietzke, S., and Schoell, M.: Global geological CH4 emission grid files, https://doi.org/10.25925/4j3f-he27, 2018.
Famiglietti, J. S.: The global groundwater crisis, Nat. Clim. Change, 4, 945–948, 2014.
Finko, E. A.: Global faults layer from ArcAtlas (ESRI), edited by: Liouty, A. A., available at: http://www.arcgis.com/home/item.html?id=a5496011fa494b99810e4deb5c618ae2#overview (last access: 30 November 2018), 2014.
Fleicher, P., Orsi, T. H., Richardson, M. D., and Anderson, A. L.: Distribution of free gas in marine sediments: a global overview, Geo-Marine Lett., 21, 103–122, 2001.
Grubbs, F.: Procedures for detecting outlying observations in samples, Technometrics, 11, 1–21, 1969.
JRC/PBL – European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC)/Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (PBL): Emission Database for Global Atmospheric Research (EDGAR), Release EDGARv4.3, available at: http://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu (last access: 30 November 2018), 2017.
Judd, A. G.: Natural seabed seeps as sources of atmospheric methane, Environ. Geol., 46, 988–996, 2004.
Judd, A. G. and Hovland, M.: Seabed Fluid Flow: Impact on Geology, Biology and the Marine Environment, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2007.
Klusman, R. W.: Rate measurements and detection of gas microseepage to the atmosphere from an enhanced oil recovery/sequestration project, Rangely, Colorado, USA, Appl. Geochem., 18, 1825–1838, 2003.
Klusman, R. W.: Baseline studies of surface gas exchange and soil–gas composition in preparation for CO2 sequestration research: Teapot Dome, Wyoming USA, Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 89, 981–1003, 2005.
Klusman, R. W., Jakel, M. E., and LeRoy, M. P.: Does microseepage of methane and light hydrocarbons contribute to the atmospheric budget of methane and to global climate change?, Assoc. Petrol. Geochem. Explor. Bull., 11, 1–55, 1998.
Klusman, R. W., Leopold, M. E., and LeRoy, M. P.: Seasonal variation in methane fluxes from sedimentary basins to the atmosphere: results from chamber measurements and modeling of transport from deep sources. J. Geophys. Res., 105D, 24661–24670, 2000.
Kvenvolden, K. A. and Rogers, B. W.: Gaia's breath global methane exhalations, Mar. Petrol. Geol., 22, 579–590, 2005.
Kvenvolden, K. A., Lorenson, T. D., and Reeburgh, W.: Attention turns to naturally occurring methane seepage, EOS, 82, p. 457, 2001.
Lacroix, A. V.: Unaccounted-for sources of fossil and isotopically enriched methane and their contribution to the emissions inventory: a review and synthesis, Chemosphere, 26, 507–557, 1993.
Lassey, K. R., Lowe, D. C., and Smith, A. M.: The atmospheric cycling of radiomethane and the “fossil fraction” of the methane source, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 7, 2141–2149, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-2141-2007, 2007.
Lelieveld, J., Crutzen, P. J., and Dentener, F. J.: Changing concentration, lifetime and climate forcing of atmospheric methane, Tellus, 50B, 128–150, 1998.
LT Environmental, Inc.: Phase II Raton basin gas seep investigation, Las animas and Huerfano counties, Colorado, Project #1925 oil and gas conservation response fund, available at: http://cogcc.state.co.us/Library/Ratoasin/Phase%20II%20Seep%20Investigation%20Final%20Report.pdf (last access: 30 November 2018), 2007.
Maasakkers, J. D., Jacob, D. J., Sulprizio, M. P., Turner, A. J., Weitz, M., Wirth, T., Hight, C., DeFigueiredo, M., Desai, M., Schmeltz, R., Hockstad, L., Bloom, A. A., Bowman, K. W., Seongeun, J., and Fischer, M. L.: Gridded national inventory of U.S. methane emissions, Environ. Sci. Technol., 50, 13123–13133, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02878, 2016.
Manga, M., Brumm, M., and Rudolph, M. L.: Earthquake triggering of mud volcanoes, Mar. Petrol. Geol., 26, 1785–1798, 2009.
Mazzini, A. and Etiope, G.: Mud volcanism: an updated review, Earth Sci. Rev., 168, 81–112, 2017.
Milkov, A. V. and Etiope, G.: Revised genetic diagrams for natural gases based on a global dataset of >20 000 samples, Org. Geochem., 125, 129–120, 2018.
Milkov, A. V., Sassen, R., Apanasovich, T. V., and Dadashev, F. G.: Global gas flux from mud volcanoes: a significant source of fossil methane in the atmosphere and the ocean, Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, 1037, https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GL016358, 2003.
Mogi, K.: Global variation of seismic activity, Tectonophysics, 57, T43–T50, 1979.
Päivi, L., Rød, J. K., and Thieme, N.: Fighting over oil: introducing a new dataset, Conflict. Manag. Peace, 24, 239–256, 2007.
Petrenko, V. V., Smith, A. M., Schaefer, H., Riedel, K., Brook, E., Baggenstos, D., Harth, C., Hua, Q., Buizert, C., Schilt, A., Mitchell, L., Bauska, T., Orsi, A., Weiss, R. F., and Severinghaus, J. P.: Minimal geological methane emissions during the Younger Dryas–Preboreal abrupt warming event, Nature, 548, 443–446, 2017.
Prather, M., Ehhalt, D., Dentener, F., Derwent, R., Dlugokencky, E., Holland, E., Isaksen, I., Katima, J., Kirchhoff, V., Matson, P., Midgley, P., and Wang, M.: Atmospheric chemistry and greenhouse gases, in climate change 2001: the scientific basis, in: Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, edited by: Houghton, J. T., Ding, Y., Griggs, D. J., Nogeur, M., van der Linden, P. J., Dai, X., Maskell, K., and Johnson, C. A., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 239–287, 2001.
Sapart, C. J., Monteil, G., Prokopiou, M., van de Wal, R. S. W., Kaplan, J. O., Sperlich, P., Krumhardt, K. M., van der Veen, C., Houweling, S., Krol, M. C., Blunier, T., Sowers, T., Martinerie, P., Witrant, E., Dahl-Jensen, D., and Röckmann, T.: Natural and anthropogenic variations in methane sources during the past two millennia, Nature 490, 85–88, 2012.
Saunois, M., Bousquet, P., Poulter, B., Peregon, A., Ciais, P., Canadell, J. G., Dlugokencky, E. J., Etiope, G., Bastviken, D., Houweling, S., Janssens-Maenhout, G., Tubiello, F. N., Castaldi, S., Jackson, R. B., Alexe, M., Arora, V. K., Beerling, D. J., Bergamaschi, P., Blake, D. R., Brailsford, G., Brovkin, V., Bruhwiler, L., Crevoisier, C., Crill, P., Covey, K., Curry, C., Frankenberg, C., Gedney, N., Höglund-Isaksson, L., Ishizawa, M., Ito, A., Joos, F., Kim, H.-S., Kleinen, T., Krummel, P., Lamarque, J.-F., Langenfelds, R., Locatelli, R., Machida, T., Maksyutov, S., McDonald, K. C., Marshall, J., Melton, J. R., Morino, I., Naik, V., O'Doherty, S., Parmentier, F.-J. W., Patra, P. K., Peng, C., Peng, S., Peters, G. P., Pison, I., Prigent, C., Prinn, R., Ramonet, M., Riley, W. J., Saito, M., Santini, M., Schroeder, R., Simpson, I. J., Spahni, R., Steele, P., Takizawa, A., Thornton, B. F., Tian, H., Tohjima, Y., Viovy, N., Voulgarakis, A., van Weele, M., van der Werf, G. R., Weiss, R., Wiedinmyer, C., Wilton, D. J., Wiltshire, A., Worthy, D., Wunch, D., Xu, X., Yoshida, Y., Zhang, B., Zhang, Z., and Zhu, Q.: The global methane budget 2000–2012, Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 8, 697–751, https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-8-697-2016, 2016.
Schwietzke, S., Sherwood, O. A., Bruhwiler, L. M. P., Miller, J. B., Etiope, G., Dlugokencky, E. J., Michel, S. E., Arling, V. A., Vaughn, B. H., White, J. W. C., and Tan, P. P.: Upward revision of global fossil fuel methane emissions based on isotope database, Nature, 538, 88–91, 2016.
Sciarra, A., Cinti, D., Pizzino, L., Procesi, M., Voltattorni, N., Mecozzi, S., and Quattrocchi, F.: Geochemistry of shallow aquifers and soil gas surveys in a feasibility study at the Rivara natural gas storage site (Po Plain, Northern Italy), Appl. Geochem., 34, 3–22, 2013.
Sherwood, O. A., Schwietzke, S., Arling, V. A., and Etiope, G.: Global Inventory of Gas Geochemistry Data from Fossil Fuel, Microbial and Burning Sources, version 2017, Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 9, 639–656, https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-639-2017, 2017.
Solomon, E. A., Kastner, M., MacDonald, I. R., and Leifer, I.: Considerable methane fluxes to the atmosphere from hydrocarbon seeps in the Gulf of Mexico, Nat. Geosci., 2, 561–565, 2009.
Tang, J. H., Bao, Z. Y., Xiang, W., and Guo, Q. H.: Daily variation of natural emission of methane to the atmosphere and source identification in the Luntai fault region of the Yakela condensed oil/gas field in the Tarim Basin, Xinjiang, China, Acta Geol. Sin., 81, 801–840, 2007.
Tang, J. H., Yin, H. Y., Wang, G. J., and Chen, Y. Y.: Methane microseepage from different sectors of the Yakela condensed gas field in Tarim Basin, Xinjiang, China, Appl. Geochem., 25, 1257–1264, 2010.
Tang, J., Xu, Y., Wang, G., Etiope, G., Han, W., Yao, Z., and Huang, J.: Microseepage of methane to the atmosphere from the Dawanqi oil-gas field, Tarim Basin, China. J. Geoph. Res.-Atmos., 122, 4353–4363, 2017.
Thornton, B. F., Geibel, M. C., Crill, P. M., Humborg, C., and Mörth, C.-M.: Methane fluxes from the sea to the atmosphere across the Siberian shelf seas, Geophys. Res. Lett., 43, 5869–5877, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL068977, 2016.
Welhan, J. A.: Origins of methane in hydrothermal systems, Chem. Geol., 71, 183–198, 1988.
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Classification of the geological CH4 sources
- Methodology
- Onshore seeps (OSs)
- Submarine seeps (SSs)
- Microseepage (MS)
- Geothermal manifestations (GMs)
- Merging OSs, SSs, MS and GMs: total geo-CH4 emission gridding
- Note on temporal variability of geological methane emissions
- Data availability
- Summary and conclusions
- Author contributions
- Competing interests
- Acknowledgements
- References
- Supplement
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Classification of the geological CH4 sources
- Methodology
- Onshore seeps (OSs)
- Submarine seeps (SSs)
- Microseepage (MS)
- Geothermal manifestations (GMs)
- Merging OSs, SSs, MS and GMs: total geo-CH4 emission gridding
- Note on temporal variability of geological methane emissions
- Data availability
- Summary and conclusions
- Author contributions
- Competing interests
- Acknowledgements
- References
- Supplement